Checkpoints
Deploy an app engine application
/ 50
Create and deploy a new version of your app
/ 50
APIs Explorer: App Engine
- GSP422
- Overview
- Setup and requirements
- Task 1. Build an App Engine application with apps.create
- Task 2. Get application information with apps.get
- Task 3. Download the starter code
- Task 4. Deploy your App Engine application
- Task 5. Configure ingress firewall rules with apps.firewall.ingressRules
- Task 6. Update your application files
- Task 7. Create a new version of your application with apps.services.versions.create
- Task 8. Deploy the new version of your application
- Congratulations!
GSP422
Overview
Google APIs Explorer is a tool that lets you try out various Google APIs interactively. With the APIs Explorer, you can:
- Browse quickly through available APIs and versions.
- See methods available for each API and what parameters they support along with inline documentation.
- Execute requests for any method and see responses in real-time.
- Make authenticated and authorized API calls.
- Search across all services, methods, and your recent requests to quickly find what you are looking for.
App Engine lets you deploy applications on a fully managed platform. You can scale your applications seamlessly without having to worry about managing the underlying infrastructure. With zero server management and zero configuration deployments, developers can focus only on building great applications without the management overhead.
In this lab you will deploy a simple hello world application to App Engine and make updates to its configuration using the App Engine Admin API through the APIs Explorer tool.
Objectives
In this lab, you will:
- Build an App Engine application with the APIs Explorer tool.
- Deploy an App Engine instance from the hello world sample code.
- Configure App Engine firewall rules with the APIs Explorer tool.
- Make changes to your code base and create a new version of your application with the APIs Explorer tool.
Prerequisites
This is a fundamental level lab. You should be familiar with the basic functioning and architecture of APIs. Experience with Google Cloud Shell and command-line interface tools is recommended.
Familiarity with the APIs Explorer tool is also recommended. At a minimum, take the following labs before attempting this one:
If you are unfamiliar with App Engine, the App Engine: Qwik Start - Python lab has valuable information that will orient you with the content of this lab. Once you're ready, scroll down and follow the steps below to set up your lab environment.
Setup and requirements
Before you click the Start Lab button
Read these instructions. Labs are timed and you cannot pause them. The timer, which starts when you click Start Lab, shows how long Google Cloud resources will be made available to you.
This hands-on lab lets you do the lab activities yourself in a real cloud environment, not in a simulation or demo environment. It does so by giving you new, temporary credentials that you use to sign in and access Google Cloud for the duration of the lab.
To complete this lab, you need:
- Access to a standard internet browser (Chrome browser recommended).
- Time to complete the lab---remember, once you start, you cannot pause a lab.
How to start your lab and sign in to the Google Cloud console
-
Click the Start Lab button. If you need to pay for the lab, a pop-up opens for you to select your payment method. On the left is the Lab Details panel with the following:
- The Open Google Cloud console button
- Time remaining
- The temporary credentials that you must use for this lab
- Other information, if needed, to step through this lab
-
Click Open Google Cloud console (or right-click and select Open Link in Incognito Window if you are running the Chrome browser).
The lab spins up resources, and then opens another tab that shows the Sign in page.
Tip: Arrange the tabs in separate windows, side-by-side.
Note: If you see the Choose an account dialog, click Use Another Account. -
If necessary, copy the Username below and paste it into the Sign in dialog.
{{{user_0.username | "Username"}}} You can also find the Username in the Lab Details panel.
-
Click Next.
-
Copy the Password below and paste it into the Welcome dialog.
{{{user_0.password | "Password"}}} You can also find the Password in the Lab Details panel.
-
Click Next.
Important: You must use the credentials the lab provides you. Do not use your Google Cloud account credentials. Note: Using your own Google Cloud account for this lab may incur extra charges. -
Click through the subsequent pages:
- Accept the terms and conditions.
- Do not add recovery options or two-factor authentication (because this is a temporary account).
- Do not sign up for free trials.
After a few moments, the Google Cloud console opens in this tab.

Activate Cloud Shell
Cloud Shell is a virtual machine that is loaded with development tools. It offers a persistent 5GB home directory and runs on the Google Cloud. Cloud Shell provides command-line access to your Google Cloud resources.
- Click Activate Cloud Shell
at the top of the Google Cloud console.
When you are connected, you are already authenticated, and the project is set to your Project_ID,
gcloud is the command-line tool for Google Cloud. It comes pre-installed on Cloud Shell and supports tab-completion.
- (Optional) You can list the active account name with this command:
- Click Authorize.
Output:
- (Optional) You can list the project ID with this command:
Output:
gcloud, in Google Cloud, refer to the gcloud CLI overview guide.
Task 1. Build an App Engine application with apps.create
You will now build an App Engine application with one of the methods found in the APIs Explorer.
-
To access the App Engine APIs Explorer tool, open up the navigation menu and select APIs & Services > Library.
-
In the search bar, enter in App Engine and select the App Engine Admin API from the results list. Make sure that API is enabled, if not click Enable.
-
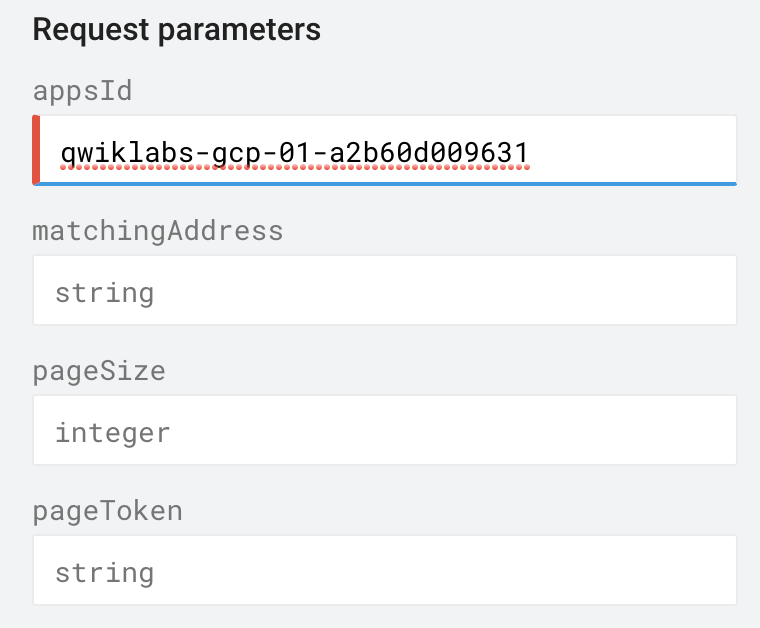
Now that you have verified the API's enablement, open the Method: apps.create reference. This will take you to the apps create method.
-
Under Try this method in the right panel, click in the Request body field and add:
- The ID property. Set it's value to your Project ID.
- The locationId property. Set its value to
. This required field tells Google Cloud where your App Engine resources will live.
- Make sure that there are no trailing spaces in any of the fields. Also, that Google OAuth 2.0 and API key checkboxes are selected under Credentials section.
-
Click the EXECUTE button.
-
Select the student account you started the lab with.
-
On the next screen, click Allow to give APIs Explorer access.
Your response should resemble the following:
You have successfully built an App Engine application for a Google Cloud project.
Task 2. Get application information with apps.get
Next you'll retrieve some information on your App Engine application to ensure that it has been properly created.
-
From the left All APIs & Reference section navigate to REST API > v1 > apps > get. Or you can use this direct link to
apps.getmethod. -
For the appsId field, enter your
<PROJECT_ID>found in the Connection Details section of the lab. -
Make sure that Google OAuth 2.0 and API key checkboxes are selected under Credentials section.
- Click the EXECUTE button. You may need to select the student account and click Allow again.
Your response should resemble the following:
This method works as a sanity check and offers you useful information about your App Engine application, such as its default hostname, location, and serving status.
Task 3. Download the starter code
Before you deploy an App Engine application, you will need to download some starter code so you have something to work with.
- Return to the Cloud Console and in Cloud Shell run the following command to clone a repository that contains the codebase for a simple hello world application:
- Now change your current working directory:
The hello_world folder contains a simple Python application that uses the Flask web framework. This Python app responds to a request with an HTTP header and the message "Hello World!"
Task 4. Deploy your App Engine application
- For this step, remain in your Cloud Shell session. Run the following command to set your Project ID as an environment variable, replacing
[YOUR_PROJECT_ID]with your Project ID:
- Now run the following gcloud command to deploy your hello world application:
- When prompted with the following, enter in Y:
The deployment will take a couple minutes to complete. Once it has finished, you should receive a similar output:
-
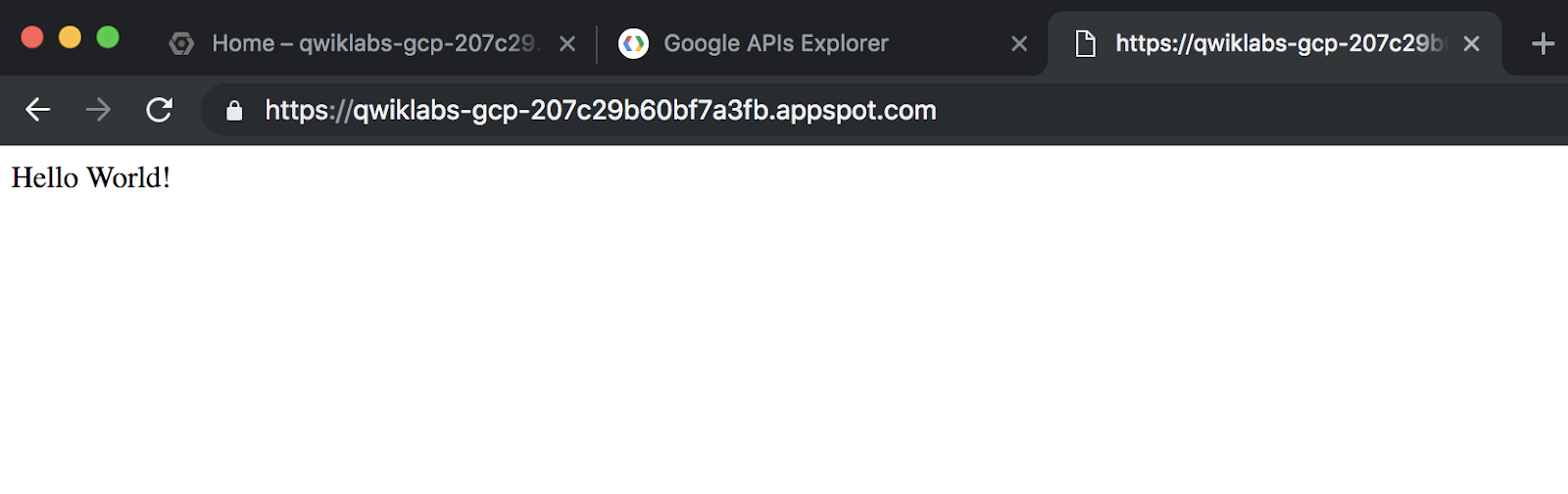
Copy the deployed service link that resembles
https://qwiklabs-gcp-b5d5fa242d334941.appspot.comand paste it in a new tab. This will open the hello world application. Your page should resemble the following:
Now that your application is deployed, you will make some changes to your App Engine configuration with the APIs Explorer.
Keep the Hello World! page open.
Test completed task
Click Check my progress to verify your performed task. If you have successfully deployed an app engine application, you will see an assessment score.
Task 5. Configure ingress firewall rules with apps.firewall.ingressRules
You will now create, list, and delete firewall rules that prescribe access to your hello world application.
Create an ingress firewall rule
-
From the APIs & Reference section navigate to REST API > v1 > apps.firewall.ingressRules > create . Or, you can use this direct link to
apps.firewall.ingressRules.createmethod. -
For the appsId field, enter your Project ID.
-
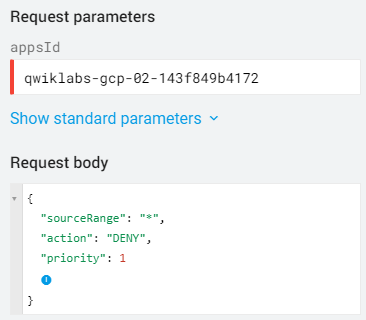
Now click on the Request body and add:
- The sourceRange property. Set it's value to
*. - The action property. Set its value to DENY.
- The priority property and set its value to 1.
Your method should resemble the following:
- Verify that your fields have no trailing spaces. Also, that Google OAuth 2.0 and API key checkboxes are selected under Credentials section.
- Click the EXECUTE button. Your response should resemble the following:
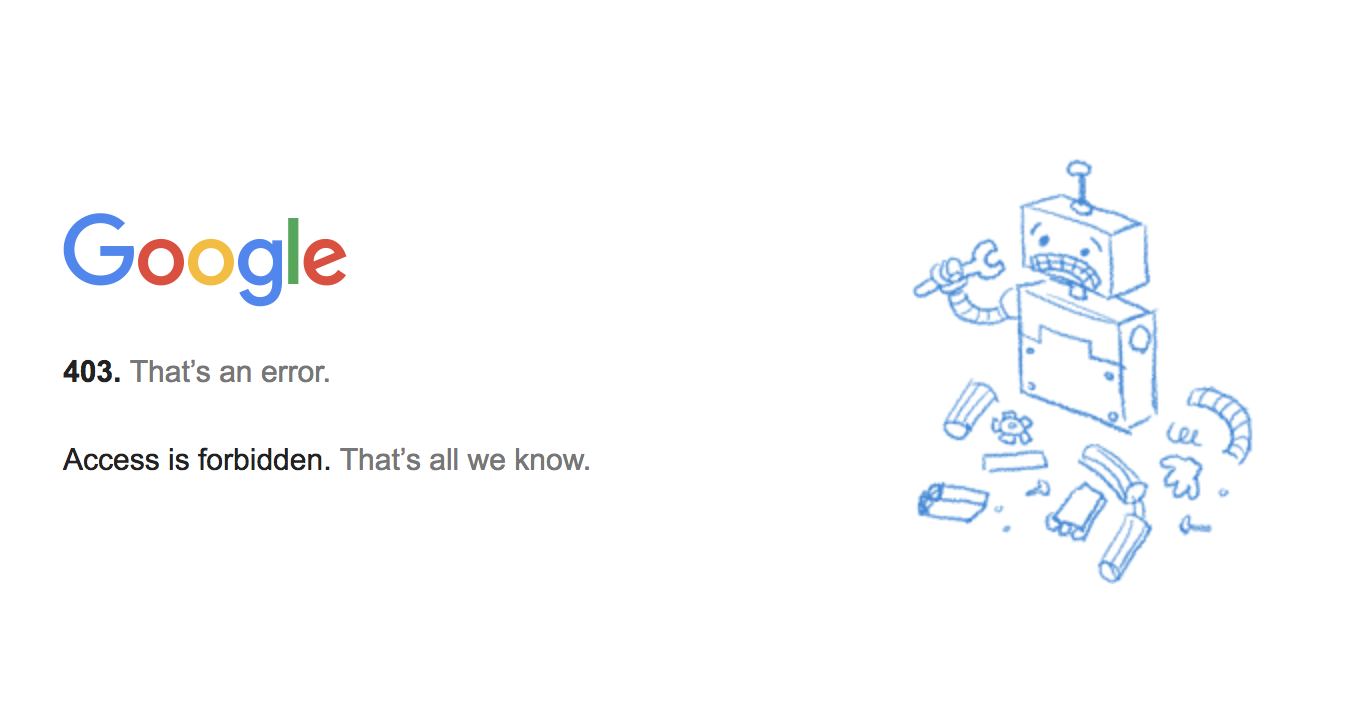
This firewall rule rejects all requests to your hello world application.
-
To see it in action, Refresh your hello world page in your browser. You should now see that access is now forbidden:
-
Return to the APIs Explorer page for the next step.
List ingress firewall rules
-
From the left All APIs & Reference section navigate to REST API > v1 > apps.firewall.ingressRules > list Or you can use this direct link to
apps.firewall.ingressRules.listmethod. -
For the appsId field, enter your Project ID.
- Verify that the appsId field has no trailing spaces. Also, that Google OAuth 2.0 and API key checkboxes are selected under Credentials section.
- Click the EXECUTE button.
Your response should resemble the following:
You now see the two firewall rules: one that allows traffic and another that denies traffic to your application. Note the priority values for each ingress rule — these act as firewall rule IDs as well.
Delete an ingress firewall rule
-
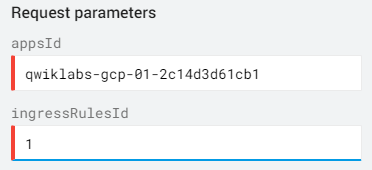
From the left All APIs & Reference section navigate to REST API > v1 > apps.firewall.ingressRules > delete Or you can use this direct link to
apps.firewall.ingressRules.deletemethod. -
For the appsId field, enter your Project ID. For the ingressRulesId field, enter 1. Your method should resemble the following:
- Verify that your fields have no trailing spaces. Also, that Google OAuth 2.0 and API key checkboxes are selected under Credentials section.
- Click the EXECUTE button.
Your response should resemble the following:
- Now refresh your hello world page in your browser. You should now see that access been restored:
Now that you've gotten practice with ingress firewall rule configuration, take it to the next level by creating and deploying new versions of our application.
Task 6. Update your application files
Now make a small change to your application's source code.
- For this step, return to the Cloud Shell. You should still be in the
hello_worlddirectory. If not, run the following command:
- Now open the
main.pyfile with thenanotext editor:
- Scroll down to the hello function and edit it so it says "Goodbye world!" instead:
- Press CNTRL +x then Y > ENTER to save your changes and exit the
nanoeditor.
Task 7. Create a new version of your application with apps.services.versions.create
You will now create a new version of your application that uses your updated "Goodbye world!" codebase.
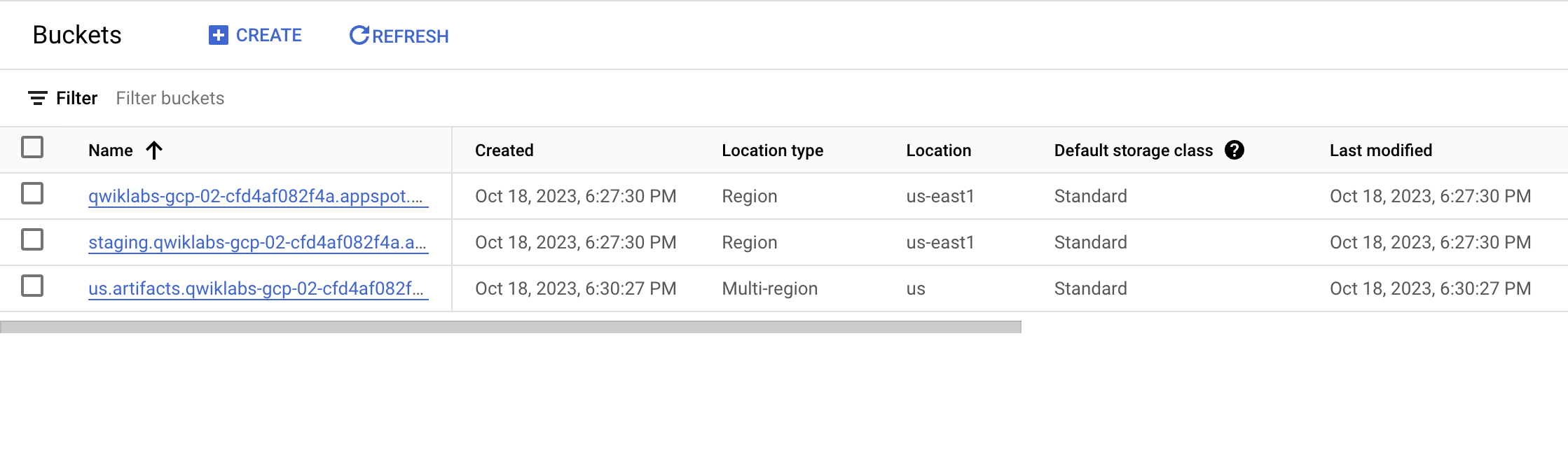
- In the Cloud Console, from the Navigation menu (
) select Cloud Storage > Buckets. You should see a list of buckets that resemble the following:
-
Copy the
staging.qwiklabs-gcp-xxxx.appspot.combucket name and save it. -
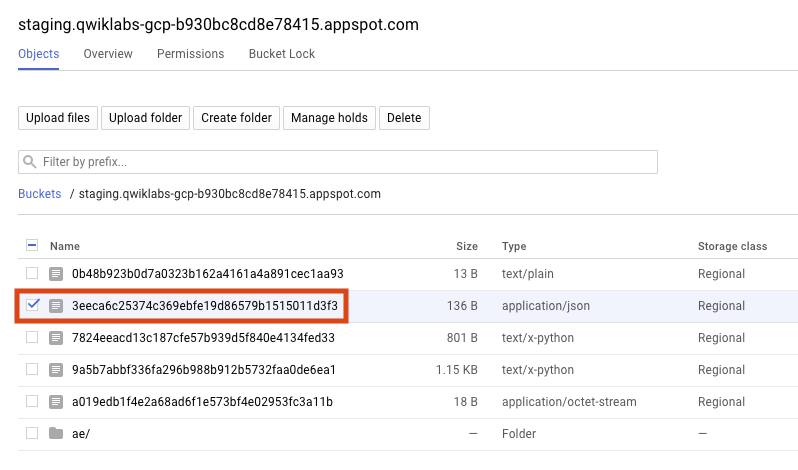
Now click on that bucket to view the files it contains.
-
Copy the name of the
application/jsonfile and save it.
You now have the information needed to create a new version of your hello world application.
-
Return to the APIs Explorer for the next step.
-
From the left All APIs & Reference section navigate to REST API > v1 > apps.services.versions > create. Or you can use this direct link to
apps.services.versions.createmethod. -
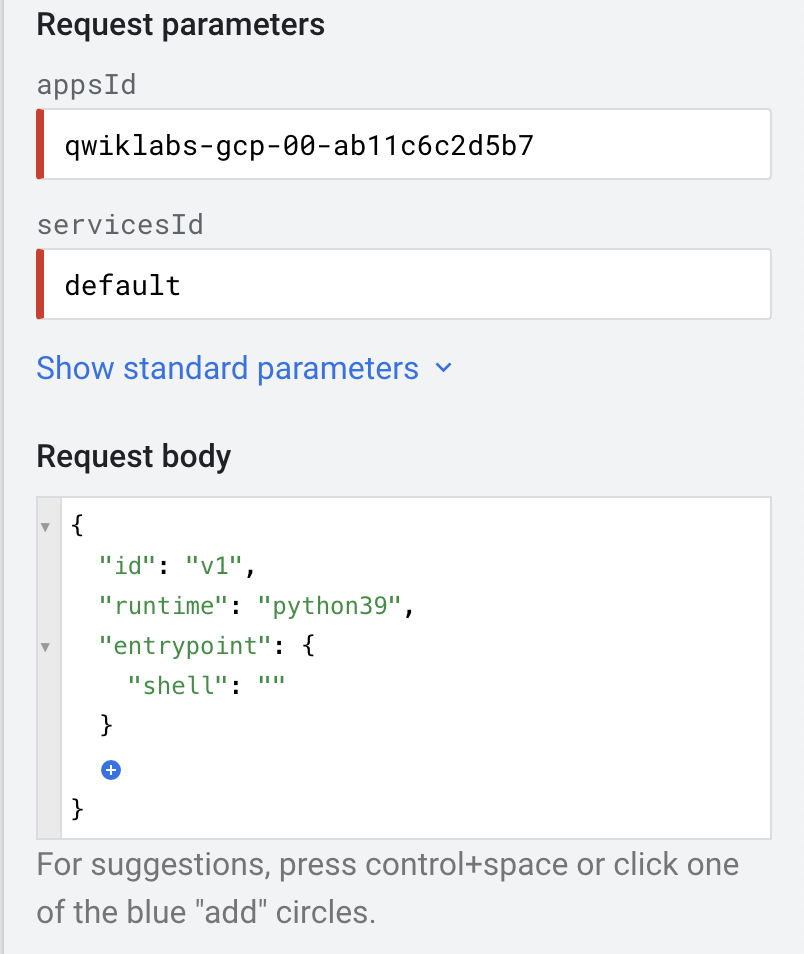
For the appsId field, enter your Project ID. For the servicesId field, enter default.
-
Now click in the request body and add:
- The id property. Set it's value to v1.
- The runtime property and set its value to python39.
- Add the entrypoint property—inside, then add the shell property and keep it's value empty.
Your method should now resemble the following:
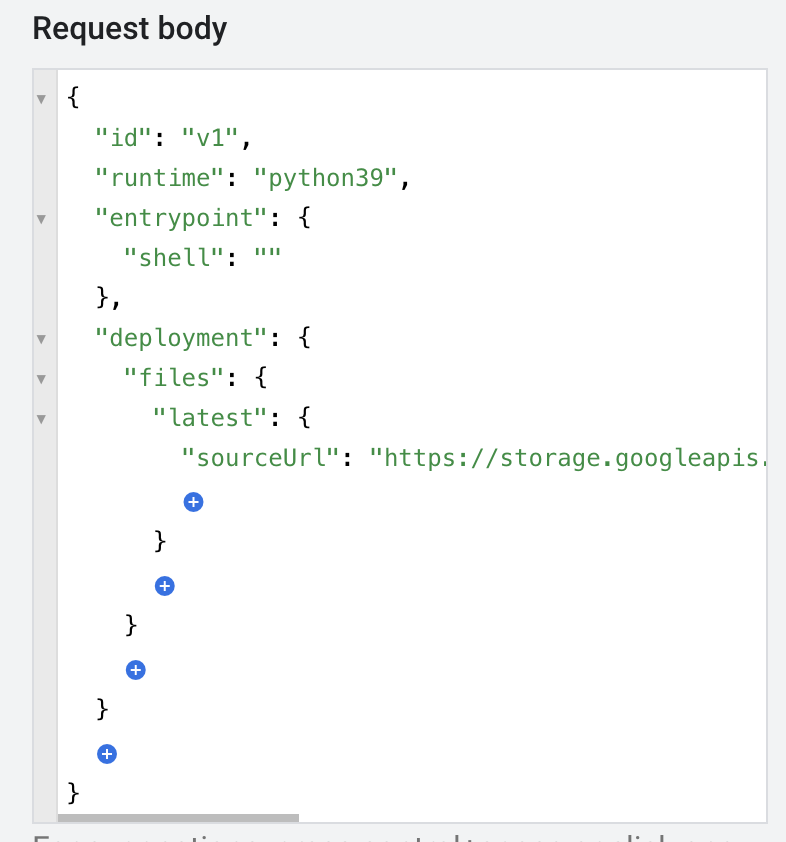
- Now add the deployment property.
- Inside deployment, add a new property files and click the add link that comes underneath it. Give it the name latest.
- Add the sourceUrl property in latest and set it to the following, replacing
<YOUR_BUCKET_NAME>with the name of the staging Cloud Storage bucket and<YOUR_JSON_FILE_NAME>with the name of the JSON file you copied over:
Your method should now resemble the following:
- Make sure that Google OAuth 2.0 and API key checkboxes are selected under Credentials section.
- Once that's filled out, click the EXECUTE button.
You should receive the following output:
There were many fields to fill out, but that is where the APIs Explorer shines. Being able to visualize all the parameters and see how they relate to one another is critical in successfully calling API methods.
Task 8. Deploy the new version of your application
-
Return to the Cloud Console for this step.
-
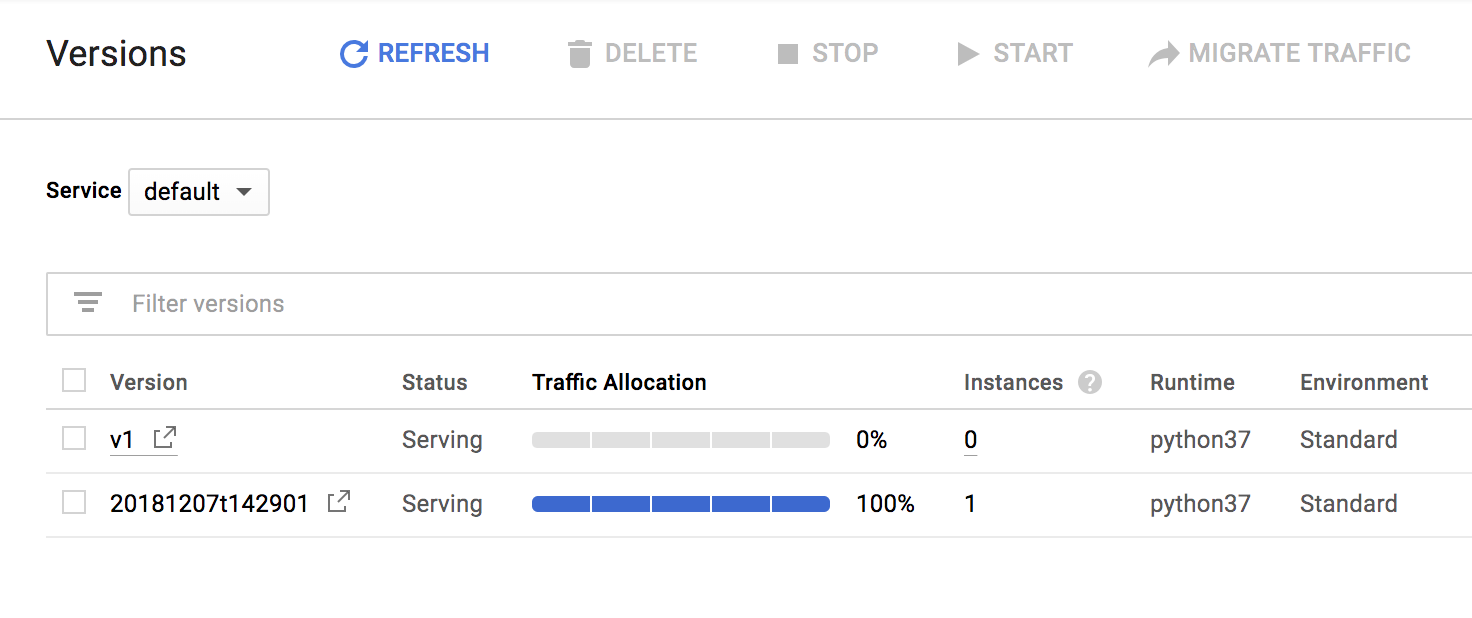
Open the navigation menu and select App Engine > Versions.
You should see that there are now two versions of your application available:
- Return to your Cloud Shell session. You should still be in the
hello_worlddirectory. If not, run the following command:
You will now deploy the new version of your application.
- Run the following command to deploy the new version, with "Goodbye world!" as the message:
- When prompted with the following, enter in Y:
The deployment will take a couple minutes to complete.
Once it has finished, you should receive a similar output:
- Now copy the link or refresh the application page in your browser. You should see the following:
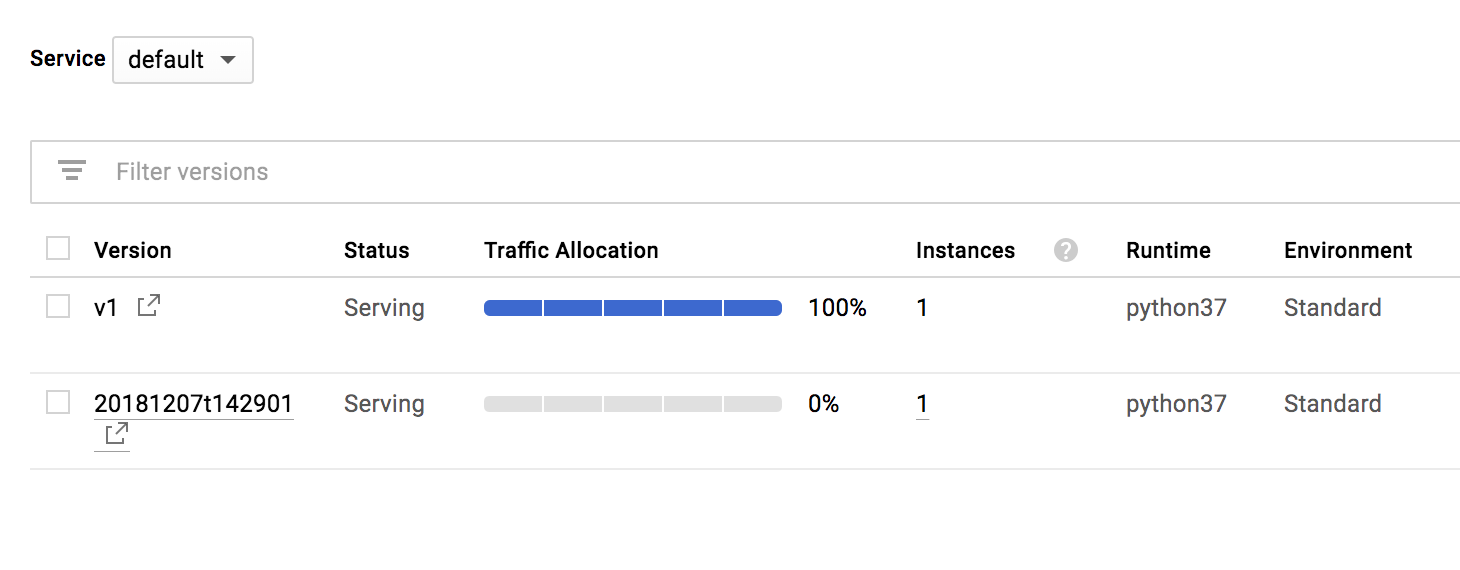
If you return to the Cloud Console and look at App Engine > Versions you will see that that v1 is being run:
You have successfully created a new version of an application with the APIs Explorer and deployed it in Cloud Shell.
Test completed task
Click Check my progress to verify your performed task. If you have successfully created a new version of your app, you will see an assessment score.
Congratulations!
In this lab, you got hands-on practice with App Engine Admin API methods using the APIs Explorer. After building an App Engine application with the APIs Explorer tool, you deployed an instance from the hello world sample code. You then learned how to configure ingress firewall rules with the APIs Explorer tool. After making changes to the codebase, you used the APIs Explorer to create a new version of your application, which you deployed and successfully accessed. You are now ready to take more Exploring APIs labs.
Finish your quest
This self-paced lab is part of the Exploring APIs quest. A quest is a series of related labs that form a learning path. Completing this quest earns you a badge to recognize your achievement. You can make your badge or badges public and link to them in your online resume or social media account. Enroll in this quest any quest that contains this lab and get immediate completion credit. See the Google Cloud Skills Boost catalog to see all available quests.
Take your next lab
Be sure to check out the following labs for more practice with the APIs Explorer:
Next steps / Learn more
- Documentation for the App Engine Admin API
Google Cloud training and certification
...helps you make the most of Google Cloud technologies. Our classes include technical skills and best practices to help you get up to speed quickly and continue your learning journey. We offer fundamental to advanced level training, with on-demand, live, and virtual options to suit your busy schedule. Certifications help you validate and prove your skill and expertise in Google Cloud technologies.
Manual Last Updated November 02, 2023
Lab Last Tested November 02, 2023
Copyright 2024 Google LLC All rights reserved. Google and the Google logo are trademarks of Google LLC. All other company and product names may be trademarks of the respective companies with which they are associated.